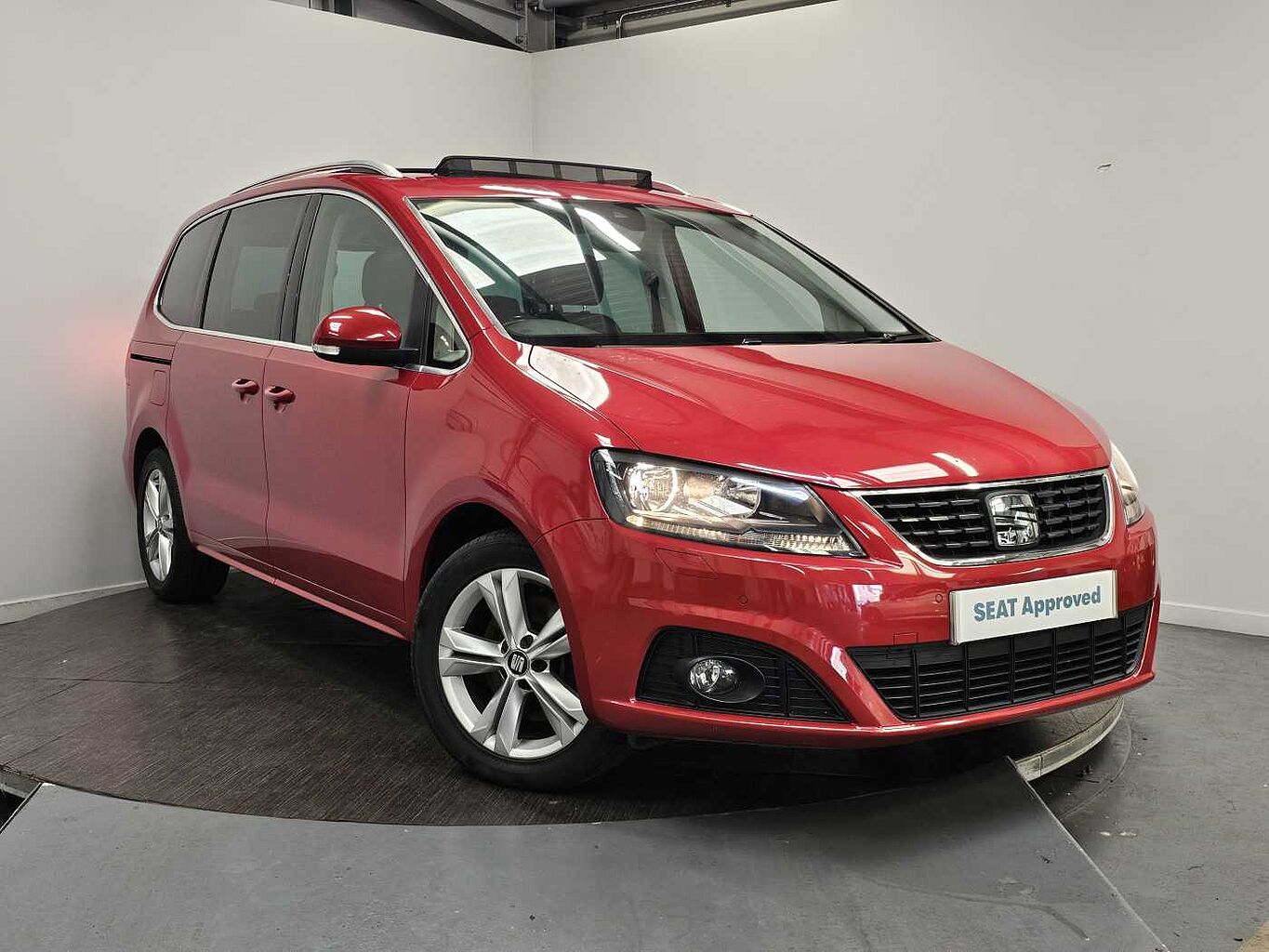
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
Diesel particulate filters reduce the number of soot particles contained in the exhaust gas, thus ensuring a further reduction in emissions and even better environmental performance of diesel engines.
At SEAT, the only system we install is maintenance-free without any additive. However, the soot deposited in the filter still needs to be disposed of so that the filter does not become clogged. For this purpose, the ceramic filter element is fitted with a noble metal-containing coating that acts in two ways.
During passive regeneration, the soot laid down in the filter is converted to CO2 in a slow, non-destructive manner. This process occurs in a temperature range of 350 - 500°C and takes place continuously, especially in motorway driving, without special measures.
Only in the event of prolonged operation at low load, for example in city traffic, approximately every 1,000 to 1,200 kilometres, does an active increase in the exhaust temperature to around 600°C take care of additional filter regeneration. At this temperature the particles accumulated in the filter burn away.
 About SEAT
About SEAT Contact Us
Contact Us